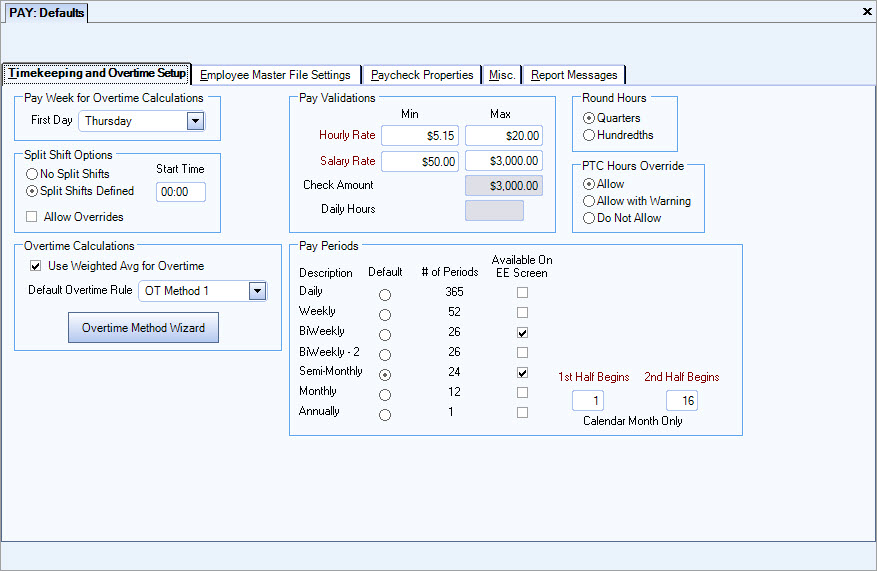
The Weighted Average option can be used to define how WinTeam determines overtime pay. With this method, when multiple pay rates exist in a pay week for an employee, WinTeam calculates a "weighted average" rate for the week. WinTeam uses the weighted average pay rate to calculate the extra 50% owed, or in the case of double-time, to calculate the extra 100% owed. To use weighted averages for calculating overtime rates, select the Use Weighted Avg for OT check box on the Payroll Defaults screen.
The most widely accepted interpretation of Wage and Hour Law as it relates to overtime, is to use the weighted average rate when computing overtime. This method stipulates that when two or more pay rates are being paid in the same pay week, the overtime pay should be computed on the basis of the weighted average weekly rate.
Weighted Average Option
If this option is used, the Payroll Check Wizard calculates the “weighted average” of an employee who has both, multiple pay rates AND overtime within the pay week. In this case, WinTeam bases the overtime rate being paid on the weighted average rate and NOT the pay rate that actually caused the overtime. The regular wages (straight wages) are still based on the normal pay rate. Only the Premium pay (the extra half time owed for Overtime or the extra 100% owed for Double-Time) is based on this weighted average.
How does the system calculate the Weighted Average Rate?
As a general rule, the weighted average rate of an employee who works at two or more different straight-time rates of pay in one workweek is the average hourly rate for the week, computed by totaling straight time pay for the week and dividing that figure by the number of hours worked. Only one-half of this rate need be paid extra for statutory overtime work in excess of the weekly hours limit (normally 40) since the normal hourly rates cover the straight-time pay.
If this check box is selected, when payroll is processed, any employee with multiple pay rates for a pay week will have their premium pay rate calculated on the weighted average rate for the week.
Important: Any hours associated with an Hours Type that set up as Exempt from Overtime Always in the Hours Type Defaults screen is NOT included in this calculation.
EXAMPLE
| Pay Week Ending 03/11/00 | Hours | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hours Type | Pay Rate | Reg | OT | DT | Exempt | Total |
| Regular | $10.00 | 32.00 | 32.00 | |||
| Sick | $10.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | |||
| Regular | $13.50 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 16.00 | ||
To figure the weighted average rate
- WinTeam ignores the Sick hours, since these hours are exempt from overtime.
- Straight-time pay is calculated for the week.
- The "weighted average rate" is calculated by dividing the straight-time pay ($536.00) by the number of hours worked (48).
- The amount per hour still owed for premium pay is then figured by dividing the "weighted average rate" in half.
- This premium amount per hour is then added to the normal pay rate.
- When the system pays the week’s wages, it will look like this:
32 hours @ $10.00/hr $320.00
16 hours @ $13.50/hr $216.00
This totals $536.00.
$536.00 divided by 48 hours = $11.1666 - rounded to $11.17
$11.17 divided in half = $5.585
| Pay Week Ending 03/11/00 | Hours | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hours Type | Pay Rate | OT Rate | Reg | OT | DT | Exempt | Total | Dollars |
| Regular | $10.00 | 32.00 | 32.00 | $320.00 | ||||
| Sick | $10.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | $80.00 | ||||
| Regular | $13.50 | $19.085 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 16.00 | $260.68 | ||
| Total Earnings | $660.68 | |||||||
Computation of the OT Rate of $19.085 using the weighted average rate
The normal pay rate determines all straight time earnings.
The only change is the figuring of their overtime rate.
Instead of being time and one half of the rate that put them into overtime, it is their normal pay rate plus ½ of the ‘weighted-average rate’.
Normal Pay Rate: $13.50
½ of Weighted Average Rate = $5.585
OT Rate therefore is = $19.085
Another alternative, is to base the overtime pay on the rate that was being used when the employee went into overtime. The system knows when someone goes into overtime as long as the hours are entered “by day".
Also, if in and out times are being entered, the system knows the “time of day” that someone went into overtime. The pay rate the employee was being paid when he went into overtime is used for figuring overtime for those particular hours, if you are not using the Weighted Average method. If there was more than one rate being paid during the week that overtime is being paid for, the employee could end up with “multiple” overtime rates.
Regulations, Part 778: Interpretative Bulletin On Overtime Compensation (part of this regulation states.) Section 778.419 Hourly workers employed at two or more jobs
Under section 7(g)(2) an employee who performs two or more different kinds of work, for which different straight time hourly rates are established, may agree with his employer in advance of the performance of the work that he will be paid during overtime hours at a rate not less than one and one-half times the hourly non-overtime rate established for the type of work he is performing during such overtime hours.
The interpretation states the employee be aware of how his/her overtime will be calculated before the performance of the work; written notification when they are hired is advised. The part referencing different kinds of work seems to be where the interpretations vary. If the employee is performing the same type of work, some argue this section does not apply, and that the rate be figured on the weighted average pay rate for the week. We suggest that you contact your own Wage and Hour office if you have any questions regarding this.
Computation of the OT Rate of $20.25 NOT using the weighted average rate
If you did not use weighted average method (without this check box selected), the system figures the overtime rate based on the pay rate that the employee was being paid when the overtime occurred. The wages would look like this:
| Pay Week Ending 03/11/00 | Hours | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hours Type | Pay Rate | OT Rate | Reg | OT | DT | Exempt | Total | Dollars |
| Regular | $10.00 | 32.00 | 32.00 | $320.00 | ||||
| Sick | $10.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | $80.00 | ||||
| Regular | $13.50 | $20.25 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 16.00 | $270.00 | ||
| Total Earnings | $670.00 | |||||||
In this case, you are actually paying more than if you had used Weighted Averaging. However, if the overtime happened to occur on the lower rate, you would be paying less than if you had used Weighted Averaging.
